How do I mount an encrypted hard drive in Linux?
- Step 1: Generate and store the keyfile. The first thing we need to do is to generate a keyfile. ...
- Step 2: Create a script returning the keyfile. ...
- Step 3: Encrypt the disk using LUKS. ...
- Step 4: Enable auto-mounting the encrypted disk.
How do I access Luks?
With LUKS encryption, you can unlock the device by interactively supplying the passphrase or automatically specifying a key file containing the passphrase to unlock the drive. To automount LUKS encrypted device in Linux, then you need to use the key file containing the passphrase.
How do I open a Luks encrypted file?
- First make your file accessible via a loopback device. losetup /dev/loop/0 /path/file.
- Open the loopback device to crypt_fun. cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/loop/0 crypt_fun.
- Mount it. mount /dev/mapper/crypt_fun /crypt.
How do I access encrypted partition?
- Step 1: Open Run dialogue (Windows + R keys), type certmgr.msc and hit Enter.
- Step 2: Open Certificate Manager > Click Personal folder in the left pane;
- Step 3: Select Action > All Tasks > Import and follow the Certificate Import Wizard.
How do I open encrypted drive in Ubuntu?
- Step 1 - Install Dislocker to Open BitLocker Drive on Linux.
- Step 2 - Create a Folder to Mount the Drive.
- Step 3 - Finding our USB Drive.
- Step 4 - Unlocking your USB Drive.
- Step 5 - Mounting your Drive.
- Step 6 - Creating a Script to automatically Mount the locked Drive.
- Conclusion.
How do I encrypt a drive with LUKS?
- dm-crypt and cryptsetup vs LUKS. dm-crypt and cryptsetup. ...
- Attach new hard disk (optional)
- Create new partition.
- Format the partition using luksFormat.
- Initialise LUKS device.
- Create file system on LUKS device.
- Mount the LUKS partition.
- Dis-connect the encrypted partition.
How do you decrypt LUKS?
- Verify that your block device has a LUKS2 header (and not LUKS1) using cryptsetup luksDump dev.
- Note what key slots are in use using cryptsetup luksDump dev.
- Reboot into a live environment using a USB stick.
- Identify your block device using blkid or lsblk .
What is a LUKS container?
The Linux Unified Key Setup (LUKS) is a disk encryption specification created by Clemens Fruhwirth in 2004 and was originally intended for Linux.
What is Luks disk encryption?
LUKS Disk Encryption. LUKS is a platform-independent disk encryption specification originally developed for the Linux OS. LUKS is a de-facto standard for disk encryption in Linux, facilitating compatibility among various Linux distributions and providing secure management of multiple user passwords.
Is Luks secure?
Yes, it is secure. Ubuntu uses AES-256 to encrypt the disk volume and has a cypher feedback to help protect it from frequency attacks and others attacks that target statically encrypted data. As an algorithm, AES is secure and this has been proved by crypt-analysis testing.
How do I know if my disk is encrypted Linux?
Another way to validate the encryption status is by looking at the Disk settings section. This status means the disks have encryption settings stamped, not that they were actually encrypted at the OS level. By design, the disks are stamped first and encrypted later.
How do you make Luks encrypted image and mount it at boot?
- Create the partition for encryption: sudo fdisk /dev/sda.
- Reboot.
- Format the partition with cryptsetup: sudo cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/sda3.
- Open encrypted partition: sudo cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sda3 secret-disk.
- Add the following to /etc/crypttab : secret-disk /dev/sda3.
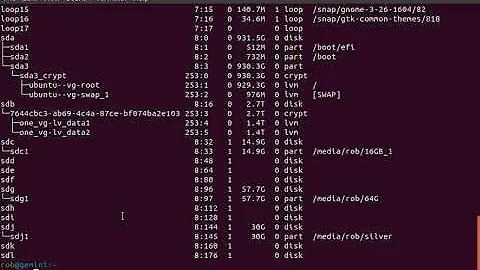
How do I mount a BitLocker partition?
- Step 1: Install Disclocker. Dislocker is available in the repositories of most Linux distributions. ...
- Step 2 : Create mount points. ...
- Step 3: Get the partition info which needs to be decrypted. ...
- Step 4: Decrypt the partition and mount.
How do I mount a BitLocker drive?
- Type in the password for the Bitlocker disk or use the recovery key file.
- Click on Mount. You will find the Bitlocker-encrypted USB drive is unlocked on the Mac computer.
How do I mount BitLocker?
- Install Dislocker. ...
- Create two folders for decrypting and mounting the BitLocker-encrypted Windows partition. ...
- Identify the partition that's encrypted using BitLocker. ...
- Decrypt and mount the BitLocker-encrypted partition on Linux.
How do I decrypt a drive in Linux?
- Enter the password or recovery key, then click "Next".
- Hasleo BitLocker Anywhere For Linux will now decrypt the contents of the selected drive using BitLocker drive encryption.
Can I open BitLocker drive on Ubuntu?
You need Dislocker to use BitLocker-encrypted drives. You can download it from here or there is a GitHub repository also.
Can I open BitLocker Drive on Linux?
This is because Linux does not support BitLocker disk encryption, so by default Linux cannot unlock BitLocker encrypted drives. To access BitLocker-encrypted drives in Linux, we have to use a third-party BitLocker solution for Linux, such as Hasleo BitLocker Anywhere For Linux or dislocker.
How do I encrypt a partition in Windows 10?
- Locate the hard drive you want to encrypt under “This PC” in Windows Explorer.
- Right-click the target drive and choose “Turn on BitLocker.”
- Choose “Enter a Password.”
- Enter a secure password.
What is Dev Mapper LUKS?
Linux Unified Key Setup (LUKS) is a specification for block device encryption. It establishes an on-disk format for the data, as well as a passphrase/key management policy. LUKS uses the kernel device mapper subsystem with the dm-crypt module.
What is Cryptsetup LUKS?
cryptsetup is used to conveniently setup dm-crypt managed device- mapper mappings. These include plain dm-crypt volumes and LUKS volumes. The difference is that LUKS uses a metadata header and can hence offer more features than plain dm-crypt. On the other hand, the header is visible and vulnerable to damage.
How do I decrypt a partition?
Open TrueCrypt and right click on the partition you want decrypted. In the right click menu, select Permanently Decrypt. You are asked whether you want to permanently decrypt the selected partition/drive. Press Yes.
How do you mount encrypted LVM logical volume?
- Initial notes. These simple instructions will work on Ubuntu Vivid Vervet and Debian Jessie. ...
- Prerequisites. ...
- Identify encrypted device. ...
- Open LUKS device. ...
- Identify volume group. ...
- List logical volumes. ...
- Activate logical volumes. ...
- Access encrypted file system.
How do I change my Luks password in Linux?
- Step 1 – Query /etc/crypttab file on Linux. ...
- Step 2 – Dump the header information of a LUKS device. ...
- Step 3 – Finding out LUKS slot assigned to you by Linux sysadmin or installer. ...
- Step 4 – Changing LUKS disk encryption passphrase in Linux using the command-line.
What is LUKS Ubuntu?
LUKS, short for Linux Unified Key Setup, is a standard hard drive encryption technology for major Linux systems including Ubuntu. It is used for encrypting entire block devices and is therefore ideal for encrypting hard disk drives, SSDs, and even removable storage drives.
References
- https://community.ebay.com/t5/Shipping/About-shipment-late/td-p/32384459
- https://support.nexo.io/hc/en-us/articles/360008117234-How-quickly-do-I-get-my-money-and-how-my-loan-transaction-will-be-referred-
- https://www.thebalancemoney.com/why-isn-t-my-money-available-at-my-bank-2385979
- https://migflug.com/jetflights/best-fighter-pilots-of-all-time/
- https://www.operationmilitarykids.org/f-22-vs-f-35-differences/
- https://export.ebay.com/en/customer-service/transactions/buyer-not-pay-item/
- https://www.alphr.com/how-much-are-tiktok-gift-points-worth/
- https://influencermarketinghub.com/tiktok-live-gifts/
- https://pages.ebay.com/sellerinformation/shipping/PPshippinglabelsfaq.html
- https://fanbytes.co.uk/buy-tiktok-followers/
- https://www.uscreen.tv/blog/how-much-does-tiktok-pay/
- https://screenrant.com/tiktok-live-lion-gift-how-much-price-explained/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lockheed_Martin_F-35_Lightning_II
- https://www.dallasnews.com/branded-content/2022/10/20/how-to-buy-tiktok-followers-the-12-best-sites-safe-growth/
- https://www.zenledger.io/blog/can-the-irs-track-crypto
- https://dailyiowan.com/2022/09/06/expose-truth-all-about-buying-tiktok-likes-and-followers-and-how-it-affects-profile/
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/do-i-have-to-pay-tax-if-i-have-pledged-my-crypto-assets-as-collateral
- https://decrypt.co/117968/nexo-says-it-has-not-given-up-on-bailout-for-rival-crypto-lender-vauld
- https://community.ebay.com/t5/Buying/Seller-won-t-ship-item-or-respond-to-messages-but-I-don-t-want-a/td-p/29616022
- https://www.thehealthyjournal.com/faq/how-do-people-cash-out-millions-in-crypto
- https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/cryptsetup.8.html
- https://www.hotcars.com/this-is-why-the-f-35-lightning-didnt-star-in-top-gun-maverick/
- https://www.golinuxcloud.com/how-to-encrypt-hard-disk-partition-luks-linux/
- https://www.salary.com/research/salary/recruiting/fighter-pilot-salary
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TikTok
- https://www.intostudy.com/en/study-abroad/country-guides/us/currency-banking
- https://help.coinbase.com/en/coinbase/trading-and-funding/buying-selling-or-converting-crypto/how-do-i-sell-or-cash-out-my-digital-currency
- https://www.ngpf.org/blog/question-of-the-day/question-of-the-day-how-much-can-a-creator-on-tiktok-make-if-their-video-receives-1-million-views/
- https://engineerine.com/fastest-planes/
- https://support-ebay.packlink.com/hc/en-gb/articles/208325869-Can-I-write-the-address-of-the-recipient-on-the-package-by-pen-
- https://teilo.org/tiktok-coins/
- https://www.ebay.com/help/buying/returns-refunds/reporting-item-didnt-receive?id=4042
- https://www.ceos3c.com/open-source/open-bitlocker-drive-linux/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linux_Unified_Key_Setup
- https://export.ebay.com/en/first-steps/how-use-ebay-seller-account/what-do-if-my-ebay-seller-account-blocked/
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/how-to-edit-remove-my-bank-account-for-usd-top-ups
- https://www.chargedretail.co.uk/2022/06/20/tiktok-influencers-are-leaving-the-platform-over-over-lack-of-payment-and-poor-quality-products/
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/does-nexo-work-on-weekends-and-holidays
- https://www.shopify.com/blog/make-money-on-tiktok
- https://www.quora.com/On-what-exchange-can-you-instantly-deposit-and-withdraw-Bitcoin-cryptocurrency
- https://itsfoss.com/mount-encrypted-windows-partition-linux/
- https://www.profit-trust.com/blog/who-is-responsible-for-a-lost-package
- https://help.coinbase.com/en/coinbase/getting-started/add-a-payment-method/instant-cashout
- https://blog.hootsuite.com/buy-tiktok-followers/
- https://www.quora.com/What-does-reporting-a-seller-on-eBay-do
- https://www.operationmilitarykids.org/best-fighter-jets-in-the-world/
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/how-to-transfer-usd-to-your-nexo-account-via-wire-transfer
- https://nexo.io/blog/nexo-announces-gradual-departure-from-the-united-states
- https://www.creditdonkey.com/nexo_coinbase.html
- https://www.distractify.com/p/how-much-is-a-rose-on-tiktok
- https://www.lockheedmartin.com/f35/news-and-features/everything-you-need-to-know-about-the-f-35c.html
- https://eurasiantimes.com/us-orders-more-air-superiority-jets-compete-against-russias-s-400/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flying_ace
- https://www.inkfrog.com/blog/eight-things-that-get-you-suspended-on-ebay-and-how-to-get-un-suspended/
- https://www.britannica.com/list/11-of-the-worlds-most-famous-warplanes
- https://www.banks.com/articles/investing/cryptocurrency/cash-out-bitcoins-without-paying-taxes/
- https://modernbattlespace.com/2022/06/15/the-f-35-helmet-a-modern-marvel-that-creates-a-unique-maintenance-challenge/
- https://www.aerotime.aero/articles/top-10-most-advanced-fighter-jets-in-2023
- https://cryptotesters.com/best-crypto-savings-accounts/nexo-review
- https://www.ebay.com/help/policies/payment-policies/unpaid-item-policy?id=4271
- https://www.cyberciti.biz/security/how-to-change-luks-disk-encryption-passphrase-in-linux/
- https://help.coinbase.com/en/coinbase/trading-and-funding/buying-selling-or-converting-crypto/how-long-does-a-sell-or-withdrawal-take-to-complete
- https://finance.yahoo.com/news/25-most-powerful-militaries-world-205638891.html
- https://theaviationgeekclub.com/us-naval-aviator-explains-why-an-f-22-pilot-out-of-gas-with-his-ejection-seat-jammed-and-its-canopy-sealed-shut-could-never-do-an-emergency-landing-on-an-aircraft-carrier/
- https://www.chargebackgurus.com/blog/ebay-chargebacks
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/how-long-does-it-take-to-get-approved-for-a-loan
- https://www.makeuseof.com/tiktok-gifts-diamonds-coins/
- https://www.tiktok.com/legal/coin-policy-eea?lang=en
- https://influencermarketinghub.com/tiktok-money-calculator/
- https://blog.elcomsoft.com/2020/08/breaking-luks-encryption/
- https://www.wikihow.com/Go-Live-on-Tiktok-Without-1000-Followers
- https://www.ebay.com/help/buying/bidding/bid-sniping?id=4224
- https://changelly.com/blog/nexo-price-prediction/
- https://carbidesecure.com/resources/how-to-encrypt-a-hard-drive-with-bitlocker-in-windows-10/
- https://www.tiktok.com/legal/virtual-items
- https://www.quora.com/Does-the-15-minute-rule-for-bidding-on-eBay-just-move-up-the-last-minute-bidding-or-sniping-war-by-15-minutes-instead-of-stop-sniping
- https://www.attentionalways.com/500k-views-on-tiktok-money/
- https://www.alphr.com/cash-out-tik-tok/
- https://www.hotcars.com/heres-why-f22-raptor-cant-be-exported/
- https://withblue.ink/2020/01/19/auto-mounting-encrypted-drives-with-a-remote-key-on-linux.html
- https://www.easyuefi.com/bitlocker-for-linux/resource/how-to-unlock-bitlocker-drive-in-linux.html
- https://www.linuxuprising.com/2019/04/how-to-mount-bitlocker-encrypted.html
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/264443/the-worlds-largest-armies-based-on-active-force-level/
- https://www.makeuseof.com/tiktok-coins-used-ways-to-spend/
- https://www.linkedin.com/in/kostakantchev
- https://www.easeus.com/storage-media-recovery/recover-data-from-encrypted-hard-drive-partition.html
- https://www.ebay.co.uk/help/policies/ebay-money-back-guarantee-policy/ebay-money-back-guarantee-policy?id=4210
- https://originstamp.com/blog/here-is-why-bitcoin-transactions-take-so-long/
- https://www.advertisemint.com/how-to-make-money-on-tiktok/
- https://sleeplessbeastie.eu/2015/11/16/how-to-mount-encrypted-lvm-logical-volume/
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/earn-daily-interest-up-to-12-apy-on-your-nexo-tokens
- https://www.coinbase.com/how-to-buy/nexo
- https://financebuzz.com/how-to-avoid-cryptocurrency-taxes
- https://jumpcloud.com/blog/how-to-enable-full-disk-encryption-on-an-ubuntu-20-04-desktop
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nexo_Knights
- https://export.ebay.com/en/fees-and-payments/payments/payment-holds/
- https://www.aura.com/learn/i-got-scammed-on-ebay-by-seller
- https://help.crypto.com/en/articles/2500695-crypto-withdrawals-general-information
- https://www.dailylocal.com/2022/07/19/buy-tiktok-followers
- https://www.thebalancemoney.com/what-to-know-about-ebay-and-paypal-fees-before-you-sell-1140371
- https://whizcase.com/how-much-is-1-coin-on-tiktok/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sixth-generation_fighter
- https://www.courierpoint.com/guides/info/refused-delivery
- https://www.tiktok.com/tiktok-rewards/benefits-rewards/
- https://www.ebay.com/help/selling/posting-items/labels-packaging-tips/buying-printing-postage-labels?id=4157
- https://byjusexamprep.com/which-country-has-the-most-advanced-military-technology-i
- https://www.ebay.com/help/selling/getting-paid/getting-paid-items-youve-sold/payments-hold?id=4816
- https://help.crypto.com/en/articles/4476691-how-do-i-cancel-or-speed-up-my-pending-eth-erc-20-transaction-on-crypto-com-defi-wallet-with-replace-by-fee
- https://www.banks.com/reviews/nexo-earn-interest-crypto/
- https://www.hotcars.com/f-35-and-f-22-comparison/
- https://www.thehealthyjournal.com/faq/does-the-f-22-have-any-kills-1
- https://support.tiktok.com/en/live-gifts-wallet/tiktok-live/live-gifts-on-tiktok
- https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/encrypting-drives-using-LUKS/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chuck_Yeager
- https://community.ebay.com/t5/Shipping/What-to-do-when-item-is-not-shipped-within-3-days-but-ebay-said/td-p/31783882
- https://support.gunbroker.com/hc/en-us/articles/221437107-15-Minute-Rule
- https://twitter.com/nexo/status/1076036860487655426
- https://www.businessinsider.com/how-much-tiktok-pays-for-views-real-examples-pulse-creator-fund
- https://www.ebay.com/help/buying/shipping-delivery/expected-delivery-dates-buyers?id=4025
- https://pro.nexo.io/fees
- https://export.ebay.com/en/customer-service/case-resolution/item-not-received-cases/
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/how-to-buy-nexo-tokens
- https://help.coinbase.com/en/coinbase/trading-and-funding/sending-or-receiving-cryptocurrency/when-will-my-digital-currency-purchase-or-local-currency-deposit-arrive
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/what-is-the-minimum-amount-of-crypto-i-can-withdraw
- https://www.digitalcitizen.life/how-decrypt-truecrypt-encrypted-drive-or-partition/
- https://www.timesofisrael.com/us-f-35-pilot-ejects-from-fighter-jet-in-texas-in-failed-landing/
- https://kifarunix.com/automount-luks-encrypted-device-in-linux/
- https://changelly.com/blog/how-to-sell-large-amounts-of-bitcoin/
- https://www.wikihow.com/Get-a-Refund-for-Late-Packages
- https://www.hotcars.com/worlds-most-powerful-air-forces/
- https://artsandculture.google.com/story/the-fastest-jet-aircraft-in-the-world-smithsonian-national-air-and-space-museum/pgUxfPwMMyO-IQ?hl=en
- https://consumer.ftc.gov/consumer-alerts/2021/11/what-do-if-your-online-order-never-arrives-and-how-get-your-money-back
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/how-do-i-withdraw-crypto-assets-i-have-stored-at-nexo
- https://web.stanford.edu/~alroth/papers/eBay.veryshortaer.pdf
- https://www.imyfone.com/make-video/how-much-does-tiktok-pay-for-1-million-views/
- https://www.easyuefi.com/bitlocker-for-linux/tutorial/decrypt-bitlocker-encrypted-drive-in-linux.html
- https://en.as.com/en/2022/02/04/latest_news/1643991315_292557.html
- https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/largest-air-forces-in-the-world
- https://303magazine.com/2022/08/buy-tiktok-followers/
- https://www.operationmilitarykids.org/f-35-vs-su-57-differences/
- https://community.ebay.com/t5/Payments/Payment-Processing-and-complete-When-do-we-ship-the-item/td-p/31341271
- https://www.shopify.com/blog/ach-withdrawal
- https://www.farukgaric.com/tiktok-gift-points/
- https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/fastest-combat-jet
- https://www.aerotime.aero/articles/30000-top-10-most-advanced-fighter-jets-of-2022
- https://publer.io/blog/how-much-do-tiktokers-make/
- https://getsby.com/en/how-to-buy-tiktok-coins-without-a-credit-or-debit-card/
- https://www.ebay.com/help/buying/returns-refunds/get-help-item-hasnt-arrived?id=4042
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/what-are-the-withdrawal-fees-for-credit-line-crypto-and-fiatx-withdrawals
- https://www.itgeared.com/how-much-are-1000-coins-on-tiktok/
- https://www.operationmilitarykids.org/navy-pilot-vs-air-force-pilot/
- https://ch.usembassy.gov/press-release-americas-most-advanced-multi-role-fighter/
- https://www.ledger.com/buy/nexo
- https://www.dexerto.com/entertainment/how-much-is-the-lion-worth-on-tiktok-1975590/
- https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/products/f-35/f-35-about.html
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/do-you-have-credit-checks-or-will-loan-from-you-affect-my-credit-score
- https://www.nicehash.com/support/general-help/wallet/why-is-my-bitcoin-deposit-taking-so-long-to-be-confirmed
- https://byjus.com/ias-questions/which-country-has-the-most-advanced-military-technology/
- https://serverfault.com/questions/515085/how-to-mount-a-luks-encrypted-file
- https://www.quora.com/Where-can-I-look-for-cheap-TikTok-coins
- https://www.nationalww2museum.org/war/articles/richard-bong-medal-of-honor
- https://www.tapology.com/rankings/3812-most-skilled-fighters-of-all-time
- https://www.cbinsights.com/company/nexo-1
- https://www.operationmilitarykids.org/navy-aircraft-fighter-jets/
- https://www.ledger.com/nexo-wallet
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lockheed_Martin_F-22_Raptor
- https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/products/f-35.html
- https://www.cryptovantage.com/news/ask-cryptovantage-how-long-does-it-take-to-send-bitcoin/
- https://askubuntu.com/questions/97196/how-secure-is-an-encrypted-luks-filesystem
- https://help.coinbase.com/en/coinbase/trading-and-funding/buying-selling-or-converting-crypto/why-does-a-sell-take-so-long
- https://export.ebay.com/en/customer-service/transactions/order-cancellation-policy/
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/how-to-deposit-crypto-assets
- https://www.dw.com/en/f-35-why-germany-is-opting-for-the-us-made-stealth-fighter-jet/a-61152127
- https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2023/02/03/tiktok-delete-advice/
- https://help.crypto.com/en/articles/6006803-24h-withdrawal-lock-on-newly-added-withdrawal-address
- https://askubuntu.com/questions/617950/use-windows-bitlocker-encrypted-drive-on-ubuntu
- https://www.wnct.com/on-your-side/consumer-watch/better-business-bureau-offers-tips-for-safe-shopping-on-tiktok/
- https://www.nationmaster.com/country-info/stats/Military/Army/Main-battle-tanks
- https://bleacherreport.com/articles/1300527-floyd-mayweather-and-the-8-most-technical-fighters-of-all-time
- https://evolve-mma.com/blog/10-of-the-most-dominant-mma-world-champions-in-history/
- https://warriormaven.com/global-security/the-top-10-fighter-jets-in-the-world-f35-f22-j20-su57-fa18-eurofighter-typhoon-f15-su35
- https://crypto.com/product-news/crypto-com-app-now-offers-instant-deposit-to-u-s-users
- https://www.demandsage.com/how-much-do-you-get-paid-on-tiktok/
- https://www.opindia.com/2022/05/indian-air-force-beats-china-to-emerge-as-third-strongest-airforce-on-global-air-power-index-of-2022/
- https://www.wikihow.com/Open-Bitlocker-Encrypted-USB-Drive-on-Another-Computer
- https://www.thehealthyjournal.com/faq/what-country-has-the-best-fighter-pilots-in-the-world
- https://www.dexerto.com/tiktok/how-to-get-cheap-tiktok-coins-1910736/
- https://www.cnbc.com/2022/09/27/crypto-lender-nexo-obtains-us-bank-charter-through-acquisition-deal.html
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/how-to-verify-encryption-status
- https://www.adda247.com/defence-jobs/strongest-air-forces-of-the-world/
- https://support.tastyworks.com/support/solutions/articles/43000435267-ach-deposit-and-withdrawal-cutoff-times
- https://www.ebay.co.uk/help/selling/getting-paid/canceling-transaction?id=4136
- https://cointelegraph.com/news/nexo-leaving-us-says-country-lacks-clear-regulations
- https://sellcoursesonline.com/how-much-money-does-tiktok-pay-for-1-million-views
- https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Removing_system_encryption
- https://www.moneyunder30.com/how-to-cash-out-bitcoin
- https://www.ebay.com/help/selling/getting-paid/resolving-unpaid-items?id=4137
- https://www.reuters.com/technology/new-york-california-sue-crypto-lender-nexo-over-interest-account-registration-2022-09-26/
- https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-12-05/crypto-lender-nexo-to-exit-us-after-facing-regulatory-scrutiny
- https://www.online-tech-tips.com/fun-stuff/top-4-ways-to-get-free-tiktok-coins/
- https://koinly.io/blog/crypto-tax-evasion/
- https://www.ebay.com/help/buying/working-sellers/seller-fraud?id=4024
- https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2022/08/27/who-has-biggest-military-world-most-powerful/7888866001/
- https://hollywoodgazette.com/2022/01/05/best-sites-to-buy-tiktok-followers/
- https://www.si.com/mma/2022/12/27/mma-pound-for-pound-rankings-top-10-fighters-2022
- https://www.ebay.co.uk/help/buying/returns-refunds/returns-missing-items-refunds-buyers?id=4008
- https://www.ndtv.com/world-news/us-air-force-to-unveil-most-advanced-military-aircraft-on-friday-5-points-3566433
- https://askubuntu.com/questions/797777/how-to-mount-a-luks-encrypted-partition-at-boot
- https://www.attentionalways.com/how-much-is-1000-coins-on-tiktok/
- https://www.liverpoolecho.co.uk/news/business/how-tiktok-shop-work-safe-25883490
- https://www.sandboxx.us/blog/the-most-important-difference-between-the-f-35-and-su-57-summed-up-in-one-picture/
- https://community.ebay.com/t5/Ask-a-Mentor/time-limit-for-shipping-after-item-was-paid-for/qaq-p/25200405
- https://www.defense.gov/News/News-Stories/Article/Article/3235326/world-gets-first-look-at-b-21-raider/
- https://www.af.mil/About-Us/Fact-Sheets/Display/Article/104506/f-22-raptor/
- https://support.nexo.io/s/article/how-do-i-withdraw-eurx-gbpx-and-usdx-from-my-nexo-account